D2d Publication: Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Kidney Function in Adults with Prediabetes: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Trial
D2d Publication: Effect of Vitamin D Supplementation on Kidney Function in Adults with Prediabetes: A Secondary Analysis of a Randomized Trial
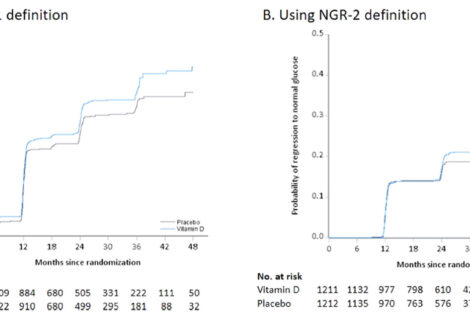
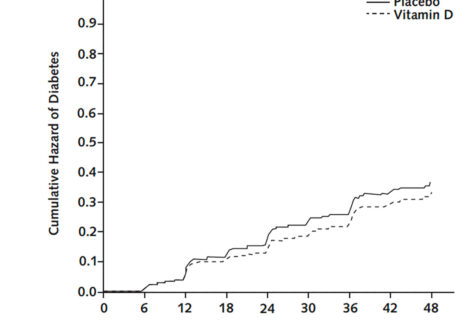
Despite evidence for associations between low circulating 25(OH)D concentration and kidney disease, few clinical trials have evaluated the effect of vitamin D supplementation on kidney outcomes. The Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes (D2d) study was a randomized clinical trial of US adults with prediabetes that tested the effect of vitamin D3 supplementation versus placebo on diabetes risk. In the D2d study, vitamin D supplementation did not significantly decrease new-onset diabetes (hazard ratio, 0.88; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.75 to 1.04); however, since publication of the main D2d results, aggregate meta-analyses have reported a significant 11%–12% reduction in diabetes risk with vitamin D supplementation among people with prediabetes. This study is a secondary analysis to determine prevalence of kidney dysfunction in the D2d prediabetes population and to examine the effect of vitamin D supplementation on incident kidney outcomes.
The manuscript was published in the Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.