CaDDM clinical trial results are published
CaDDM clinical trial results are published
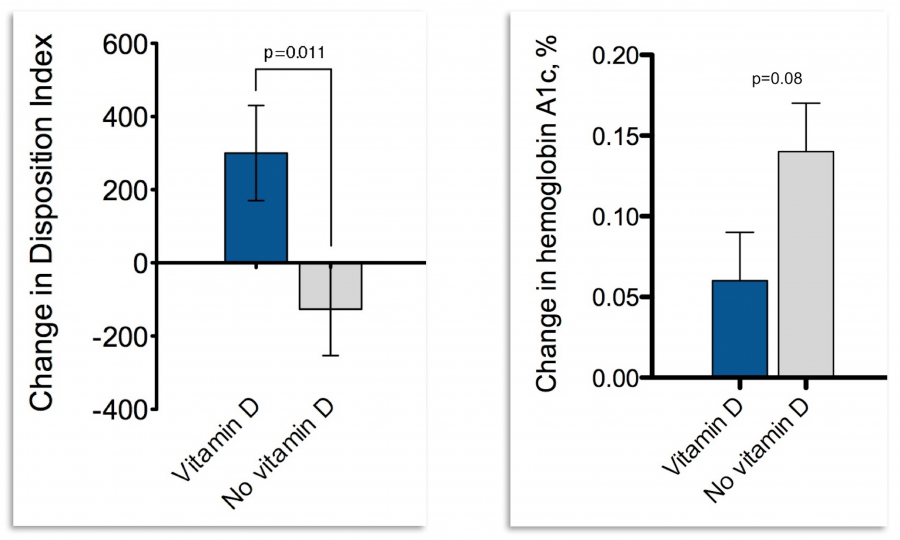
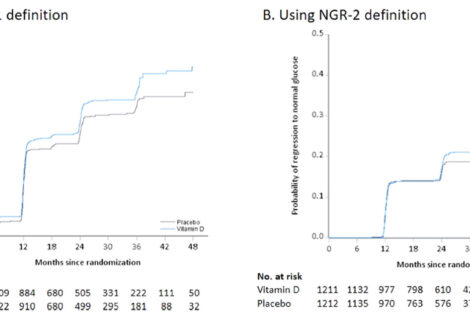
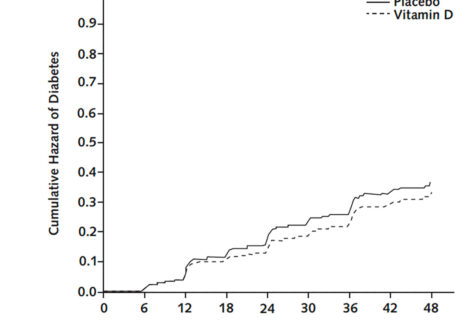
Results of the Vitamin D and Calcium Homeostasis for Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes (CaDDM) study support a mechanistic link between vitamin D and diabetes risk among adults at risk for diabetes or with early diabetes not requiring medications. In the CaDDM study, which was a randomized controlled clinical trial, vitamin D supplementation for 4 months increased blood 25-hydroxyvitamin D level by ~12 ng/mL and improved disposition index by ~26% vs. worsening of disposition index ~14% in the placebo group (p=0.011). Importantly, although the CaDDM study was not powered for glycemic outcomes, hemoglobin A1c level – a measure of average glucose levels in the blood over the past 3 months – was lower in the vitamin D group by about 0.08. Although this difference seems small, it can have a sizeable effect at the public health level. Calcium supplementation alone did not have any significant effect.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) and the Office of Dietary Supplements (ODS) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Results were published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.